Navigating the Depths of Multimedia Filtration in Water Treatment
Multimedia filtration emerges as a formidable player in the arena of water treatment, employing a diverse array of materials and a strategic layering approach to achieve optimal purification. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the intricacies of multimedia filter water treatment, unraveling the nuances of sediment removal, tank design, and the overall effectiveness of this versatile filtration system.

1. The Essence of Multimedia Filtration: An Overview
At the heart of multimedia water treatment lies a nuanced filtration process designed to target particles of varying sizes. The key components include:
Granular Materials: Unlike single-media filters, multimedia filters utilize a mix of granular materials such as sand, anthracite, and garnet. This diverse combination allows for the removal of both large and fine particles.
Layered Structure: The filter tank is carefully filled with these granular materials in distinct layers. Each layer plays a specific role in the filtration process, ensuring a comprehensive treatment of water from various sources.

2. Unraveling the Sediment Removal Potential
Multimedia sediment filters are engineered to address the challenge of sedimentation in water sources. Sediment, consisting of suspended particles and impurities, can compromise water quality. Here's how multimedia filtration tackles this issue:
Mechanical Filtration: The sand layer in multimedia filters acts as a mechanical barrier, capturing larger particles and preventing them from progressing further into the filtration system.
Fine Particle Removal: The subsequent layers, including anthracite and garnet, focus on finer particles. This multilayered approach ensures that sediments of varying sizes are effectively removed, resulting in clarified and purified water.

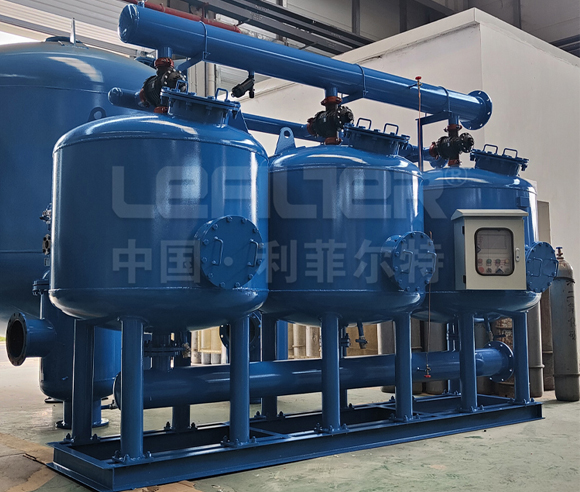
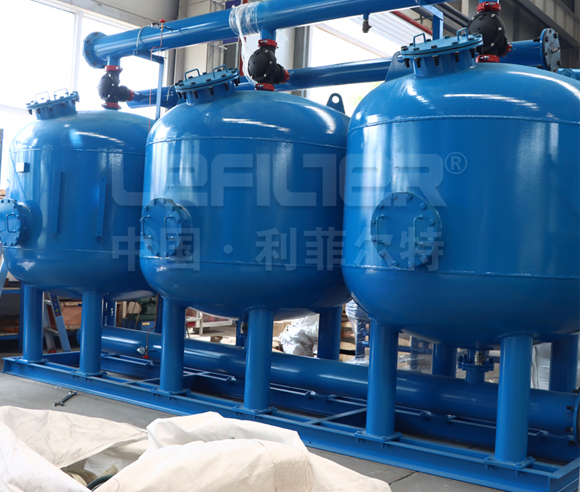
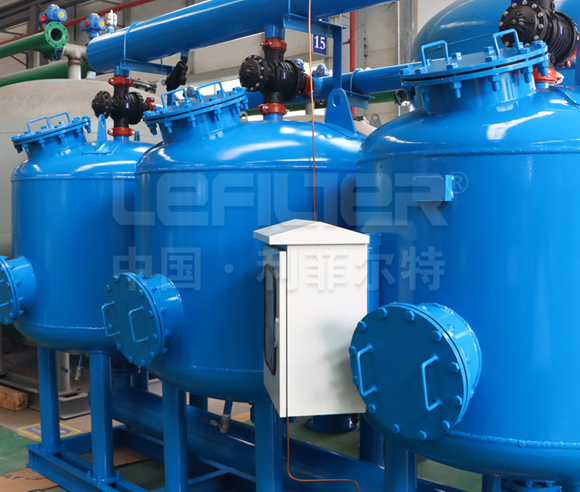
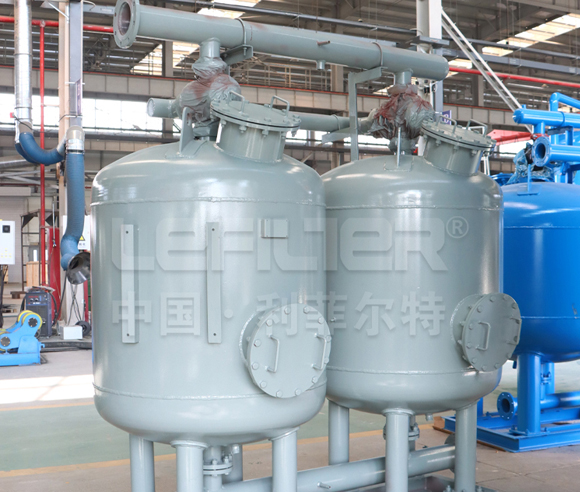
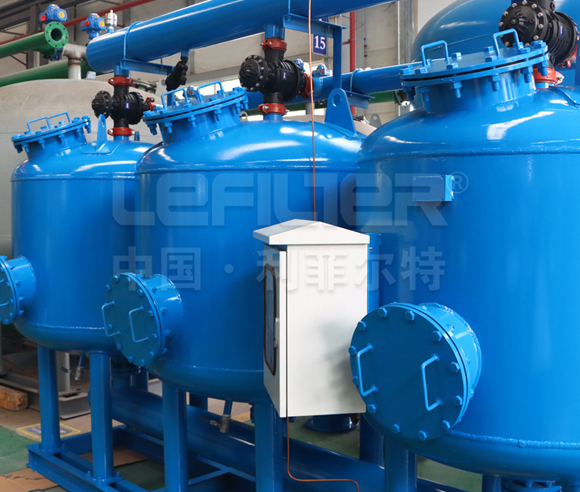
3. The Anatomy of Multimedia Filter Tanks
The design of the filter tank is pivotal in determining the efficiency of multimedia water treatment. Key considerations include:
Tank Size and Shape: The dimensions of the tank influence the contact time between water and filter media. Larger tanks accommodate more filter media, enhancing the filtration capacity.
Distribution Systems: Effective distribution of water across the filter bed is essential. Multimedia filter tanks are equipped with distribution systems that ensure even water flow, optimizing the filtration process.
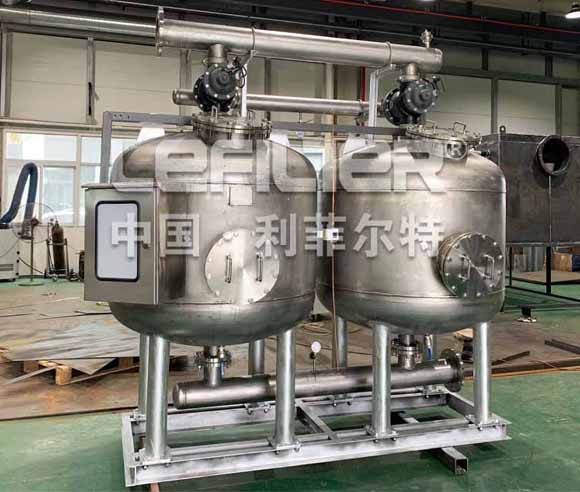

4. Water Multimedia Filters: Versatility Unleashed
Water multimedia filters extend their reach beyond sediment removal, showcasing versatility in various water treatment applications:
Municipal Water Treatment: In municipal settings, multimedia filters are employed to treat water from diverse sources, providing communities with clean and potable water.
Industrial Processes: Industries benefit from multimedia filtration in processes where water quality is paramount, preventing equipment damage and ensuring product quality.
Wastewater Treatment: Multimedia filters play a crucial role in wastewater treatment, removing contaminants and particulate matter before discharge.
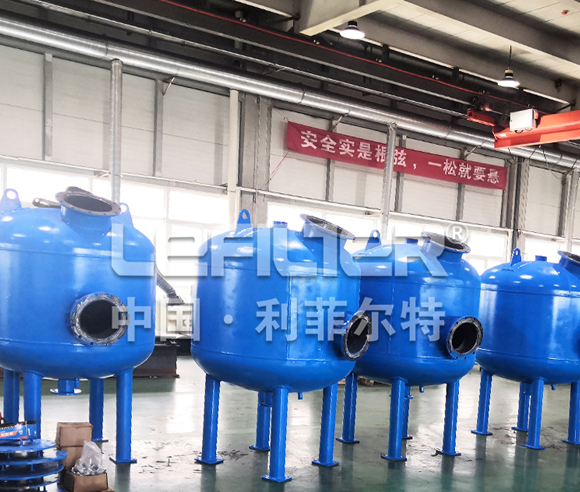

5. Sustainability in Multimedia Filtration
In addition to its effectiveness, multimedia filtration aligns with sustainability goals in several ways:
Reduced Backwashing Frequency: The layered design allows multimedia filters to operate efficiently with less frequent backwashing, conserving water and minimizing energy consumption.
Longevity: With proper maintenance, multimedia filters can have an extended lifespan, contributing to sustainable water treatment practices.

Conclusion: Navigating the Waters with Multimedia Filtration
As we navigate the complexities of water treatment, multimedia filtration emerges as a beacon of efficiency and versatility. From sediment removal to diverse applications across industries, the layered design of multimedia filters proves its mettle. As communities and industries seek robust solutions for water purification, the multifaceted approach of multimedia filtration stands as a testament to its effectiveness and adaptability in the ever-evolving landscape of water treatment.